How does gasoline engine work?
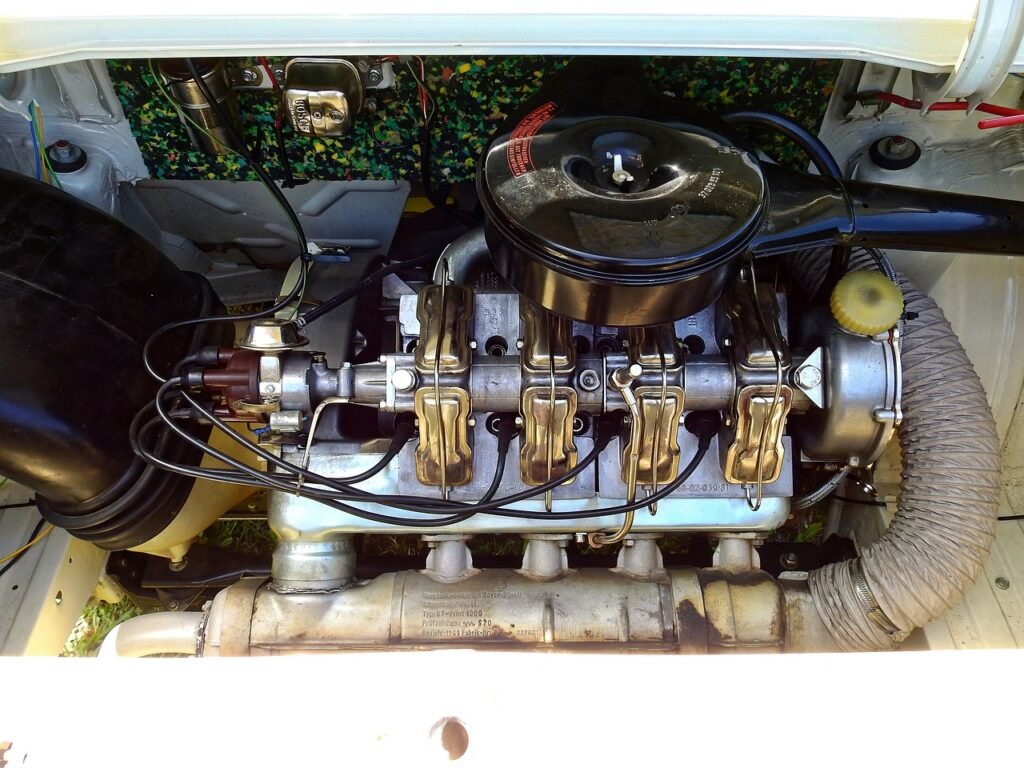

Understanding the intricacies of a gasoline engine is not just a matter of theory; it’s a journey into the heart of automotive engineering that has evolved over decades. While the core principles remain consistent, technological advancements have propelled gasoline engines into a realm of efficiency unimaginable years ago. In this article, we’ll embark on a detailed exploration of how a gasoline engine works, refreshing your memory on the theory and shedding light on the marvels of modern automotive engineering.
The Essence of a Gasoline Engine: Unveiling the Basics
At its core, a gasoline engine is an internal combustion engine featuring a piston. The process begins with the intake stroke, where a precise mixture of gasoline and air is injected into the engine cylinder. This concoction undergoes compression in the next stroke, elevating both pressure and temperature within the cylinder. The pivotal moment comes with the electric spark ignition, setting off a rapid combustion of the fuel mixture. This combustion generates gases that exert force, driving the piston and translating energy into mechanical work.
The ingenious crank mechanism steps in to convert the linear movement of the piston into a rotary motion, giving birth to the power pulse that propels the engine. The intricate dance of linear piston movements, the jolt drive, and the conversion of linear to rotary motion form the symphony that powers the vehicle. As the gears connect to the drive shafts, the motion cascades to the wheels, setting the vehicle in motion.
Demystifying the Piston Dynamics: A Symphony of Linear and Rotary Motion
Within the confines of the engine, a series of meticulously orchestrated movements take place. Picture four pistons housed in cylinders, each executing a dance between upper and lower points. The pressure created by igniting the air-fuel mixture triggers the linear movement of the piston, initiating the engine’s dynamic cycle.
The crucial components facilitating this orchestration are the injector or vaporizer, responsible for “brewing” the air-fuel mixture, and a set of valves regulating the suction and expulsion of gases. As the piston moves linearly, it sets the crankshaft in motion, which, in turn, orchestrates the seamless conversion of linear motion into a powerful rotary force. This rotary motion, akin to a mechanical heartbeat, is then transmitted to the vehicle’s wheels, setting the entire mechanism in motion.
Maintenance: The Lifeblood of Engine Longevity
A gasoline engine, like any intricate machinery, demands regular and attentive maintenance to ensure its longevity and optimal performance. Key maintenance tasks include checking and changing the engine oil, among other critical components. The engine’s symbiotic relationship with fuel, cooling, ignition, and electrical systems requires meticulous attention.
Regular maintenance serves as a preventive measure against accelerated wear and tear, safeguarding the engine from potential breakdowns. Issues such as poor fuel mixtures, lack of spark, or compression problems can be averted through diligent maintenance practices. By adhering to the manufacturer’s guidelines and scheduling routine check-ups, one ensures the engine’s robust health, enabling it to function at its peak potential.
The gasoline engine is a marvel of engineering, blending fundamental principles with cutting-edge technology. As we traverse the intricate landscape of its workings, we unveil not just the mechanics but the artistry that propels our vehicles forward. Embracing the evolution of gasoline engines, we recognize that every revolution of the crankshaft is a testament to the ingenuity that powers our modern modes of transportation.